这两年用 GitHub 越来越多,不管是拉源码、下依赖还是看项目,网络状态好坏差别非常明显。有时候网页能打开,但 clone、release 下载速度慢得离谱,甚至直接超时。
以前也试过各种加速方式,有的要装客户端,有的需要代理环境,对普通电脑环境来说反而麻烦。最近自己顺手写了一个小脚本,思路很简单:自动更新本机 hosts 文件,把 GitHub 相关域名指向可用的 IP,再顺便刷新一次 DNS 缓存。
脚本运行一次就完成,不需要常驻,也不需要额外软件,适合偶尔需要加速 GitHub 的场景。
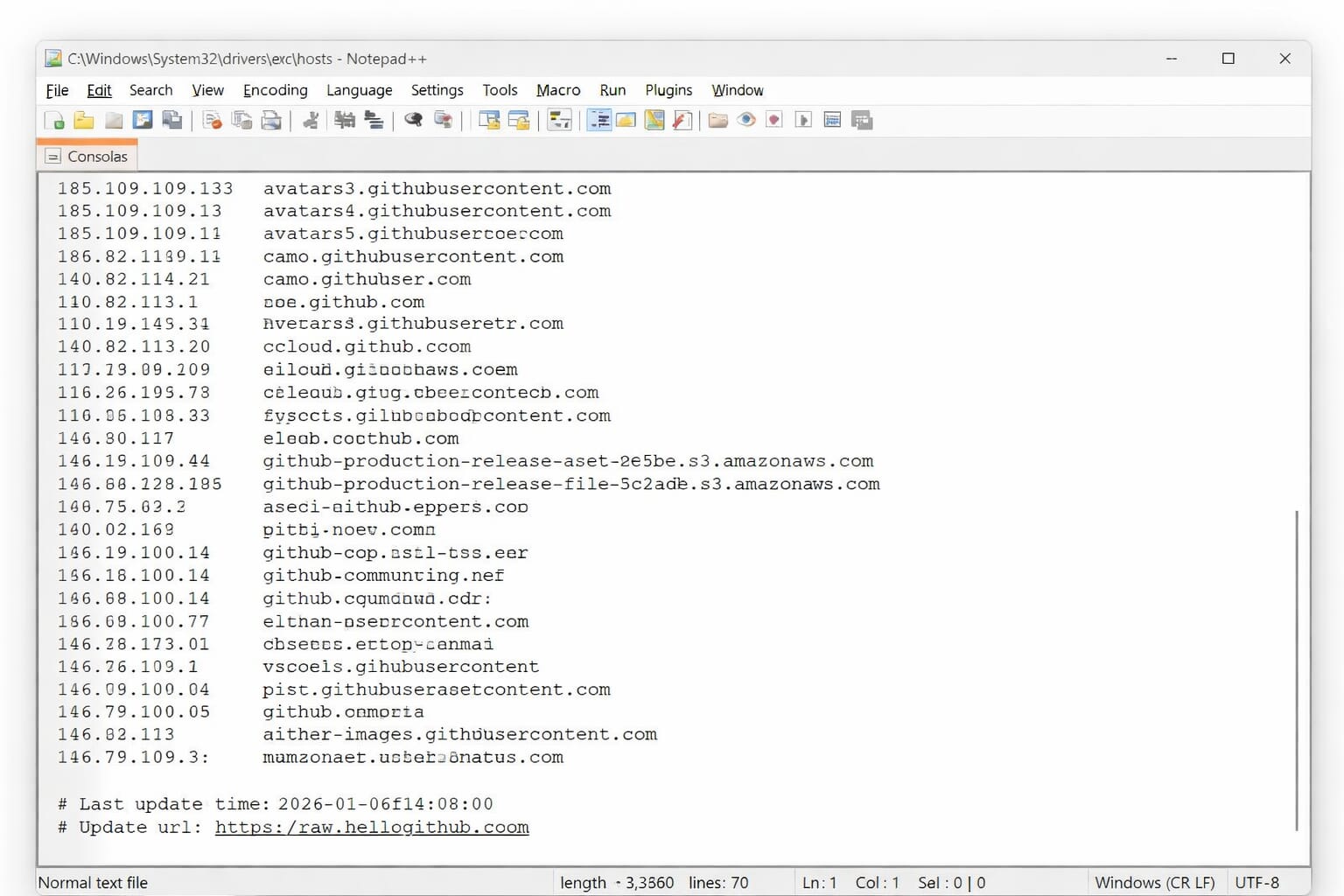
从截图可以看到,hosts 文件已经被自动写入了一批 GitHub 相关域名映射。脚本执行时窗口会闪一下,很快就结束,实际上已经完成了修改。
修改完成后重新打开浏览器访问 GitHub,或者再执行 git clone,一般速度都会明显改善。如果网络环境变化,再运行一次即可自动刷新。
这个方式本质上还是利用 hosts 强制解析,并不是万能方案,但在多数情况下还是很实用的,尤其是在临时环境、测试机、虚拟机上,省去一堆配置过程。
脚本是用 Python 写的,逻辑也比较直观:
先从远端获取最新的 hosts 内容,读取本地原有 hosts,清理旧标记段,然后写入新的内容,最后自动刷新 DNS 缓存,避免系统还在使用旧解析结果。
下面是完整源码,方便有需要的朋友自行修改或二次使用。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import sys
import urllib.request
import re
import subprocess
# 配置
HOSTS_URL = "https://raw.hellogithub.com/hosts"
LOCAL_HOSTS_PATH = {
"nt": r"C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts",
"posix": "/etc/hosts"
}.get(os.name, "/etc/hosts")
GITHUB_HOSTS_MARK = "# GitHub520 Host Start"
END_MARK = "# GitHub520 Host End"
def fetch_latest_hosts():
try:
print("正在获取最新 hosts 配置...")
with urllib.request.urlopen(HOSTS_URL, timeout=15) as resp:
content = resp.read().decode('utf-8')
return content
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取 hosts 失败: {e}")
return None
def read_current_hosts():
try:
with open(LOCAL_HOSTS_PATH, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
return f.read()
except Exception as e:
print(f"无法读取 hosts 文件: {e}")
return None
def flush_dns_cache():
"""跨平台刷新 DNS 缓存"""
print("正在刷新 DNS 缓存...")
try:
if os.name == 'nt': # Windows
subprocess.run(
["ipconfig", "/flushdns"],
check=True,
stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL,
stderr=subprocess.DEVNULL
)
elif sys.platform.startswith('darwin'): # macOS
subprocess.run(
["sudo", "dscacheutil", "-flushcache"],
stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL,
stderr=subprocess.DEVNULL
)
subprocess.run(
["sudo", "killall", "-HUP", "mDNSResponder"],
stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL,
stderr=subprocess.DEVNULL
)
else: # Linux
services = ["systemd-resolved", "nscd"]
for svc in services:
try:
if svc == "systemd-resolved":
subprocess.run(
["sudo", "resolvectl", "flush-caches"],
check=True,
stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL,
stderr=subprocess.DEVNULL
)
elif svc == "nscd":
subprocess.run(
["sudo", "systemctl", "restart", "nscd"],
stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL,
stderr=subprocess.DEVNULL
)
break
except:
continue
print("DNS 缓存已刷新")
except Exception as e:
print(f"刷新 DNS 时出现异常(可忽略): {e}")
def write_hosts(new_content):
try:
with open(LOCAL_HOSTS_PATH, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(new_content)
print("hosts 文件已更新")
flush_dns_cache()
except PermissionError:
print("权限不足,请以管理员权限运行")
sys.exit(1)
except Exception as e:
print(f"写入 hosts 失败: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
def is_admin():
"""判断是否具有管理员权限"""
if os.name == 'nt':
try:
import ctypes
return ctypes.windll.shell32.IsUserAnAdmin() != 0
except:
return False
else:
return os.geteuid() == 0
def main():
print("GitHub hosts 自动更新工具")
if not is_admin():
if os.name == 'nt':
print("请右键选择“以管理员身份运行”")
else:
print("请使用 sudo 运行脚本")
sys.exit(1)
new_hosts = fetch_latest_hosts()
if not new_hosts:
sys.exit(1)
current_hosts = read_current_hosts()
if current_hosts is None:
sys.exit(1)
# 清理旧标记内容
pattern = re.compile(
re.escape(GITHUB_HOSTS_MARK) + r".*?" + re.escape(END_MARK),
re.DOTALL
)
cleaned_hosts = pattern.sub("", current_hosts).strip()
final_hosts = cleaned_hosts + "\n\n" + new_hosts.strip() + "\n"
write_hosts(final_hosts)
print("操作完成,现在可以重新访问 GitHub 了")
input("按回车键退出...")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
脚本运行时需要管理员权限,这是因为 hosts 文件本身属于系统保护文件。如果权限不足,脚本会直接提示。
如果你只是想简单使用,直接打包成 exe 后双击运行即可;如果是技术人员,也可以根据自己的网络环境改成定时更新、自动任务等玩法。
整体来说,这是一个偏实用的小工具,不追求复杂功能,核心目标只有一个:尽量减少 GitHub 访问过程中的等待时间。
对于经常需要拉源码、同步仓库、测试项目的环境来说,还是挺省心的。
工具信息说明
工具名称:GitHub 网络访问优化脚本
适用系统:Windows(管理员权限运行)
运行形式:可打包为单文件程序或直接运行 Python 脚本
体积大小:约 6MB(打包后)
主要作用:自动更新 hosts 并刷新 DNS 缓存
适合场景:开发环境、测试机、临时网络优化
下载地址:





![[Windows] AI 小说生成器 V1.0|智能小说生成系统(附使用说明)](https://www.hanzijs.com/wp-content/themes/ceomax-pro/timthumb.php?src=https://www.hanzijs.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/df3038488ebdde65b80f0d6246d9356a.png&h=200&w=300&zc=1&a=t&q=100&s=1)